Maraming Salamat po sa author at nagshare nito sa amin.
Kong rePOST na po idedelete ko na lang po ito.
Suggestion and correction are welcome.
1. Definition and Terms
AGP - Accelerated Graphics Port. An old slot type for graphics cards. AGP graphics cards are too slow for modern games. You won't see this anymore on modern motherboards. AGP graphics cards will only fit in AGP slots. Replaced by PCI-E
Benchmark - a test or set of tests that measure performance of a PC. Synthetic applications or real-world applications can be used for benchmarks. Benchmarks are mostly used by overclockers to measure the performance gained by overclocking. It can also be used to measure the performance gain of a hardware upgrade
BIOS - Basic Input and Output System. When updating your BIOS, make sure your PC is plugged on a UPS. If the BIOS update process is interrupted by a power failure, the BIOS will be corrupted. Your PC will not function if this is damaged or corrupted.
CPU - Central Processing Unit. This is the brain of the PC. This is commonly called as the processor
CPU Frequency - This shows how fast a CPU is and it has a unit of Gigahertz (GHz). Higher is better for the same family of processors
CPU Socket - This is where the CPU chip fits in. AMD processors use AM2, AM2+, and AM3 while Intel processors use LGA 775, LGA 1156, and LGA 1366
Cool n Quiet - Power saving feature of AMD processors. The CPU downclocks when it is idle or the load is light
CrossFire - A technology from ATi that allows 2 or more ATi GPU's to work together in games
EIST - Enhanced Intel Speed Step. Power saving feature of Intel processors. The CPU downclocks when it is idle or the load is light
FSB - Front Side Bus. Old Intel CPU's and all LGA 775 CPU's use the FSB to communicate with the memory.
HDD - Hard Disk Drive. Used as primary data storage
HSF - Heat Sink and Fan. This cools the CPU. Too much heat and your CPU will die sooner than expected.
IGP - Integrated Graphics Processor. AMD IGP's are located on the motherboard and modern Intel IGP's are located on the CPU chip. IGP's are not advisable for gaming
IMC - Integrated Memory Controller
LCD - Liquid Crystal Display. A type of display that is replacing CRT monitors. Have a low power consumption compared to CRT monitors
LGA - Land Grid Array. A socket type used by modern Intel processors. The contact pins are on the motherboard.
GPU - Graphics Processing Unit. This comes in two types, IGP and Add-on. Add-on type of GPU's are those cards that you insert in the AGP slot or PCI-E slot
Overclocking - The process of running a component beyond its rated speed. Should be done with caution. Overclocking can damage your components if not done properly
PGA - Pin Grid Array. A CPU socket type used by AMD processors
PCI-E - Peripheral Component Interconnect Express. Used by modern graphics cards
PSU - Power Supply Unit. This is the part that supplies power to every component of your PC. Make sure you use a reliable PSU to ensure safe and stable operation of your PC.
RAM - Random Access Memory. Commonly called as memory.
SLI - Scalable Link Interface. A technology from nVIDIA that allows 2 or more nVIDIA GPU's to work together in games
SSD - Solid State Drive. Similar to HDD's except there are no more mechanical parts. It is a lot faster than HDD's but still very expensive to replace HDD's
UPS - Uninterruptible Power Supply. In case of a power failure, this provides backup power for your PC to give you enough time to save your files and properly shut down your PC.
2. Choosing the Right CPU
When choosing your CPU or processor, know first the applications that you will be using and don't rely on the specifications of the processor. The core count and CPU frequency is not a reliable measure of performance. The best way to compare performance of different CPU's is to run a benchmark using real-world applications. A fast dual-core processor will do if you will do mostly gaming, web browsing, file downloading, some video trancoding, and other light tasks like typing documents. If you will use the PC for heavy tasks like 3D rendering, lots of video transcoding, and file compression, a quad-core processor or six-core CPU will serve you better. AMD also makes triple-core CPU'ss which offers performance in between duals and quads.
Naming Scheme of CPU's
- 2 cores -
AMD Phenom II X2
AMD Athlon II X2
Intel Pentium Dual Core
Intel Core 2 Duo
Intel Core i3 500 series
Intel Core i5 600 series
Intel Core i3 2000 series
- 3 cores -
AMD Phenom II X3
AMD Athlon II X3
- 4 cores -
AMD Phenom II X4
AMD Athlon II X4
Intel Core i5 700 series
Intel Core i7 800 series
Intel Core i7 900 series
Intel Core i5 2400 series
Intel Core i5 2500 series
Intel Core i7 2600 series
- 6 cores -
AMD Phenom II X6
Intel Core i7 970
Intel Core i7 980X
Intel Core i7 990X
All Intel Core i series CPU's have Turbo Boost except for Core i3
All Intel Core i series CPU's have Hyper Threading Technology except for Core i5 700 series, Core i5 2400 series, and Core i5 2500 series.
AMD Athlon II series does not have L3 Cache
>> List of Recommended CPU's <<
- Entry Level -
AMD Athlon II X2 250 3.0 GHz
AMD Athlon II X3 440 3.0 GHz
AMD Athlon II X4 640 3.0 GHz
Intel Core i3 530 2.93 GHz
- Mainstream -
AMD Phenom II X2 555BE 3.2 GHz
AMD Phenom II X4 955BE 3.2 GHz
AMD Phenom II X4 965BE 3.4 GHz
AMD Phenom II X6 1055T 2.8 GHz
Intel Core i5 750 2.66 GHz
Intel Core i5 760 2.8 GHz
Intel Core i5 2500K 3.3 GHz
- High End -
AMD Phenom II X6 1090T 3.2 GHz
Intel Core i7 870 2.93 GHz
Intel Core i7 930 2.8 GHz
Intel Core i7 2600K 3.4 GHz
3. Getting the Right Motherboard
Tips on motherboard layout
View attachment 36281
1. Make sure the CPU socket type is compatible with the CPU you will be using
AM3/AM2+
- Phenom II
- Athlon II
LGA 775
- Pentium Dual Core
- Core 2 Duo
- Core 2 Quad
LGA 1156
- Core i3 500 series
- Core i5 600 series
- Core i5 700 series
- Core i7 800 series
LGA 1155
- Core i3 2000 series
- Core i5 2000 series
- Core i7 2000 series
LGA 1366
- Core i7 900 series
- Core i7 970
- Core i7 980X
2. Make sure the main 24-pin connector is located along the edge of the board. Avoid boards where the main 24-pin connector is located near the CPU socket
3. Take note of the position of the sATA ports. If you are planning on using gaming graphics cards, make sure the sATA ports are not in line with the PCI-E slots. If ever the sATA ports are in line with a PCI-E slot, make sure they are in a parallel position with respect to the board like the black sATA ports of the MSI P55-GD80 pictured above. However, there are some casings where you need the sATA ports to be perpendicular with respect to the board.
4. As much as possible, choose a board where the CMOS battery is located far from the PCI slots and PCI-E slots
5. If the budget is not restricted, select a board that uses solid capacitors. Solid capacitors are more tolerant to heat compared to electrolytic capacitors. They also have a longer life span and they don't leak.
6. For convenience, choose a board that has a CMOS reset button. Some boards even a feature a CMOS reset button located at the rear panel so you don't have to open the casing if ever you need to reset the CMOS
What Chipset Should I Choose?
The motherboard usually has 2 chipsets
1. Northbridge - for Intel LGA 775, it holds the Memory Controller and the PCI-E Controller. The Northbridge determines the type, maximum amount, and maximum speed of memory. It also determines the number of PCI-E lanes that will be available.
2. Southbridge - it handles the Input/Output devices (keyboard, mouse, gamepads), storage devices (HDD, SSD, USB) and other components of the PC
Modern AMD and Intel CPU's now have an Integrated Memory Controller. So it is now the CPU that determines the type, maximum amount, and maximum speed of memory. The Northbridge is now only left with the function of supplying the PCI-E lanes. Modern CPU's don't use the FSB anymore, they now communicate directly with the memory
For Intel LGA 1156 motherboards, there is only one main chip - the Platform Controller Hub. It functions more like a Southbridge and the 2 common chipsets are P55 and H55. The main difference between P55 and H55 is that H55 allows the use of IGP's of Intel Core i3 500 and Core i5 600. Using a Core i3 500 or Core i5 600 on a P55 board is possible but the IGP will be disabled. All LGA 1156 processors are compatible with P55 and H55.
Intel LGA 1366 boards still has two chips- the Northbridge and the Southbridge. It only has one type of Northbridge - the X58. The X58 chipset has 36 PCI-E lanes but this becomes only significant in a multi-GPU setup.
List of Recommended Motherboards
- Entry Level -
ASRock N68C-S (AM3 / AM2+)
ASRock 880GM-LE (AM3)
MSI 785G-E53 (AM3)
ASRock P55 Pro (LGA 1156)
eVGA H55-V (LGA 1156)
- Mainstream -
ASRock 890GX Extreme 3 (AM3)
MSI 890GXM-G65 (AM3)
Asus M4A89GTD PRO/USB3 (AM3)
MSI H55-GD65 (LGA 1156)
MSI P55-GD65 (LGA 1156)
MSI P55-GD80 (LGA 1156)
eVGA P55 SLI (LGA 1156)
eVGA X58 SLI Micro (LGA 1366)
- High End -
Asus Crosshair IV Formula (AM3)
MSI Big Bang Fuzion (LGA 1156)
MSI Big Bang X Power (LGA 1366)
4. Memory Speed, Type and Amount
Form Factor
These are the types of memory according to form factor. The form factor indicates the size of the module and the number of contact pins
1. SIMM - Single In-line Memory Module. It can either have 30 pins or 72 pins.
2. DIMM - Dual In-line Memory Module. This is the form factor used by modern desktop PC's. It can have a 184-pin configuration or a 240-pin configuration. Modern desktop PC's use DIMM's
3. SODIMM - Small Outline DIMM. Used by laptop PC's. It can have a 72-pin configuration or 144-pin configuration
4. MicroDIMM - smaller than SODIMM
Types of Desktop DIMM
DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM)
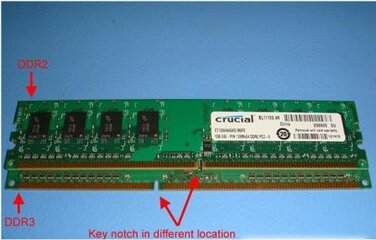
1. DDR2 (1.8V) - used by Intel LGA 775 CPU's and AMD AM3/AM2+ CPU's
2. DDR3 (1.35V to 1.65) - used by Intel LGA 1156 CPU's, LGA 1366 CPU's and AMD AM3 CPU's
View attachment 36282
(DDR3 modules can only be installed in a DDR3 slot and DDR2 modules can only be installed in a DDR2 slot)
Modern PC's should have a minimum of 2GB RAM especially if you intend to use it for gaming. If there are no restrictions on the budget, go for 4GB. But I recommend you get two 2GB modules instead of one 4GB module. This would come in handy if ever one of the modules fail. If you do heavy multi-tasking, go for 6GB or 8GB.
If you are building a new PC, there si really no need to go for DDR2 because the price of the DDR2 and DDR3 are almost the same. But in terms of real world performance, DDR2 and DDR3 perform equally at the same DRAM frequency
Most manufacturers sell dual-channel kits. These are ordinary modules but they already come in pairs so you won't have compatibility issues. So, if you plan on using two memory modules, get a dual-channel kit instead of buying two separate memory modules. By the way, Intel LGA 1366 CPU's use triple-channel DDR3 modules so check before buying to avoid compatibility issues.
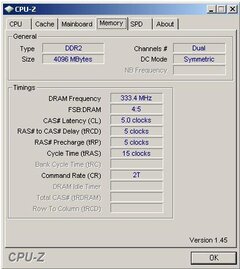
To check if dual channel mode is enabled, you can see it at the boot up screen or you can use CPU-Z. See image below for a sampe of CPU-Z screenshot
View attachment 36283
What Memory Speed Should I Choose ?
For the memory speed, DDR3 1333 and DDR3 1600 will do for real world applications. Only synthetic benchmarks will benefit from DDR3 1800 or higher
+ Test System +
Intel Core i7 870
Asus Maximus III Formula
Corsair 2GBx2 DDR3 1600
Zotac GeForce GTX 260
Windows Vista Enterprise Version 64-bit
WinRar 3.9 beta 64-bit - File Compression (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 117.4
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 114.9
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 110.2
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 103.8
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
WinZip 12 - File Compression (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 102.1
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 101.4
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 101.0
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 100.3
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
Adobe Acrobat 9 Professional - PDF document creation (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 101.1
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 101.1
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 101.1
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 101.1
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
Adobe Photoshop CS4 - Image Processing - Applying 6 filters to a 69MB TIF image (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 101.0
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
Lame 3.98 - Audio encoding - wav to mp3 160kbps (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
DivX 6.8.3 - Video transcoding - MPEG2 to AVI (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 103.6
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 102.4
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 102.4
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 101.2
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
3DS Max 2009 - Image rendering - 1920 x 1080 (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 101.3
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 101.3
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 100.7
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
Memory Clock Speed and Data Transfer Rate
Memory - Real Clock - Effective Clock - Maximum Theoretical Data Rate - Memory Module
DDR 200 - 100 MHz - 200 MHz - 1600 MB/s - PC-1600
DDR 266 - 133 MHz - 266 MHz - 2133 MB/s - PC-2100
DDR 333 - 166 MHz - 333 MHz - 2666 MB/s - PC-2700
DDR 400 - 200 MHz = 400 MHz - 3200 MB/s - PC-3200
DDR2 400 - 200 MHz - 400 MHz - 3200 MB/s - PC2-3200
DDR2 533 - 266 MHz - 533 MHz - 4266 MB/s - PC2-4200
DDR2 667 - 333 MHz - 667 MHz - 5333 MB/s - PC2-5300
DDR2 800 - 400 MHz - 800 MHz - 6400 MB/s - PC2-6400
DDR2 1066 - 533 MHz - 1066 MHz - 8533 MB/s - PC2-8500
DDR3 800 - 400 MHz - 800 MHz - 6400 MB/s - PC3-6400
DDR3 1066 - 533 MHz - 1066 MHz - 8533 MB/s - PC3-8500
DDR3 1333 - 667 MHz - 1333 MHz - 10666 MB/s - PC3-10600
DDR3 1600 - 800 MHz - 1600 MHz - 12800 MB/s - PC3-12800
DDR3 1800 - 900 MHz - 1800 MHz - 14400 MB/s - PC3-14400
DDR3 2000 - 1000 MHz - 2000 MHz - 16000 MB/s - PC3-16000
Effective Clock = Real Clock x 2
Maximum Theoretical Data Rate = Effective Clock x 8
Memory modules manufacturers usually name their mmodules according to the Effective Clock but some use the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
How to Read Part Numbers of Memory Modules
Kingston
Part Number: KHX1600C7D3K2/4GX
--> KHX means Kingston HyperX
--> 1600 is the Effective Clock
--> C7 is the CAS Latency
--> D3 means DDR3
--> K2 means 2 modules
--> 4G is the total capacity of the modules
This is a Kingston HyperX 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL7
Kingston
Part Number: KHX1333C7D3K3/6GX
--> KHX means Kingston HyperX
--> 1333 is the Effective Clock
--> C7 is the CAS Latency
--> D3 means DDR3
--> K3 means 3 modules
--> 6G is the total capacity of the modules
This is a Kingston HyperX 2GBx3 DDR3 1333 CL7
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL9D-4GBRL
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL9 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> D means dual channel, 2 modules
--> 4GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> R stands for Ripjaws
--> L means Ripjaws rated at 1.5V
This is a G. Skill Ripjaws 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL9
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL8D-4GBRM
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL8 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> D means dual channel, 2 modules
--> 4GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> R stands for Ripjaws
This is a G. Skill Ripjaws 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL8
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL8Q-8GBRM
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL8 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> Q means dual channel, 4 modules
--> 8GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> R stands for Ripjaws
This is a G. Skill Ripjaws 2GBx4 DDR3 1600 CL8
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL7D-4GBRH
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL7 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> D means dual channel, 2 modules
--> 4GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> R stands for Ripjaws
This is a G. Skill Ripjaws 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL7
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL8D-4GBTD
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL8 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> D means dual channel, 2 modules
--> 4GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> T stands for Trident
This is a G. Skill Trident 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL8
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL7T-6GBRH
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL7 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> T means triple channel, 3 modules
--> 6GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> R stands for Ripjaws
This is a G. Skill Ripjaws 2GBx3 DDR3 1600 CL7
Corsair
Part Number: CMG4GX3M2A1600C7
--> 1600 is the Effective Clock
--> C7 is the CAS Latency
--> 4G is the total capacity of the modules
This is a Corsair 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL7
Kong rePOST na po idedelete ko na lang po ito.
Suggestion and correction are welcome.
1. Definition and Terms
AGP - Accelerated Graphics Port. An old slot type for graphics cards. AGP graphics cards are too slow for modern games. You won't see this anymore on modern motherboards. AGP graphics cards will only fit in AGP slots. Replaced by PCI-E
Benchmark - a test or set of tests that measure performance of a PC. Synthetic applications or real-world applications can be used for benchmarks. Benchmarks are mostly used by overclockers to measure the performance gained by overclocking. It can also be used to measure the performance gain of a hardware upgrade
BIOS - Basic Input and Output System. When updating your BIOS, make sure your PC is plugged on a UPS. If the BIOS update process is interrupted by a power failure, the BIOS will be corrupted. Your PC will not function if this is damaged or corrupted.
CPU - Central Processing Unit. This is the brain of the PC. This is commonly called as the processor
CPU Frequency - This shows how fast a CPU is and it has a unit of Gigahertz (GHz). Higher is better for the same family of processors
CPU Socket - This is where the CPU chip fits in. AMD processors use AM2, AM2+, and AM3 while Intel processors use LGA 775, LGA 1156, and LGA 1366
Cool n Quiet - Power saving feature of AMD processors. The CPU downclocks when it is idle or the load is light
CrossFire - A technology from ATi that allows 2 or more ATi GPU's to work together in games
EIST - Enhanced Intel Speed Step. Power saving feature of Intel processors. The CPU downclocks when it is idle or the load is light
FSB - Front Side Bus. Old Intel CPU's and all LGA 775 CPU's use the FSB to communicate with the memory.
HDD - Hard Disk Drive. Used as primary data storage
HSF - Heat Sink and Fan. This cools the CPU. Too much heat and your CPU will die sooner than expected.
IGP - Integrated Graphics Processor. AMD IGP's are located on the motherboard and modern Intel IGP's are located on the CPU chip. IGP's are not advisable for gaming
IMC - Integrated Memory Controller
LCD - Liquid Crystal Display. A type of display that is replacing CRT monitors. Have a low power consumption compared to CRT monitors
LGA - Land Grid Array. A socket type used by modern Intel processors. The contact pins are on the motherboard.
GPU - Graphics Processing Unit. This comes in two types, IGP and Add-on. Add-on type of GPU's are those cards that you insert in the AGP slot or PCI-E slot
Overclocking - The process of running a component beyond its rated speed. Should be done with caution. Overclocking can damage your components if not done properly
PGA - Pin Grid Array. A CPU socket type used by AMD processors
PCI-E - Peripheral Component Interconnect Express. Used by modern graphics cards
PSU - Power Supply Unit. This is the part that supplies power to every component of your PC. Make sure you use a reliable PSU to ensure safe and stable operation of your PC.
RAM - Random Access Memory. Commonly called as memory.
SLI - Scalable Link Interface. A technology from nVIDIA that allows 2 or more nVIDIA GPU's to work together in games
SSD - Solid State Drive. Similar to HDD's except there are no more mechanical parts. It is a lot faster than HDD's but still very expensive to replace HDD's
UPS - Uninterruptible Power Supply. In case of a power failure, this provides backup power for your PC to give you enough time to save your files and properly shut down your PC.
2. Choosing the Right CPU
When choosing your CPU or processor, know first the applications that you will be using and don't rely on the specifications of the processor. The core count and CPU frequency is not a reliable measure of performance. The best way to compare performance of different CPU's is to run a benchmark using real-world applications. A fast dual-core processor will do if you will do mostly gaming, web browsing, file downloading, some video trancoding, and other light tasks like typing documents. If you will use the PC for heavy tasks like 3D rendering, lots of video transcoding, and file compression, a quad-core processor or six-core CPU will serve you better. AMD also makes triple-core CPU'ss which offers performance in between duals and quads.
Naming Scheme of CPU's
- 2 cores -
AMD Phenom II X2
AMD Athlon II X2
Intel Pentium Dual Core
Intel Core 2 Duo
Intel Core i3 500 series
Intel Core i5 600 series
Intel Core i3 2000 series
- 3 cores -
AMD Phenom II X3
AMD Athlon II X3
- 4 cores -
AMD Phenom II X4
AMD Athlon II X4
Intel Core i5 700 series
Intel Core i7 800 series
Intel Core i7 900 series
Intel Core i5 2400 series
Intel Core i5 2500 series
Intel Core i7 2600 series
- 6 cores -
AMD Phenom II X6
Intel Core i7 970
Intel Core i7 980X
Intel Core i7 990X
All Intel Core i series CPU's have Turbo Boost except for Core i3
All Intel Core i series CPU's have Hyper Threading Technology except for Core i5 700 series, Core i5 2400 series, and Core i5 2500 series.
AMD Athlon II series does not have L3 Cache
>> List of Recommended CPU's <<
- Entry Level -
AMD Athlon II X2 250 3.0 GHz
AMD Athlon II X3 440 3.0 GHz
AMD Athlon II X4 640 3.0 GHz
Intel Core i3 530 2.93 GHz
- Mainstream -
AMD Phenom II X2 555BE 3.2 GHz
AMD Phenom II X4 955BE 3.2 GHz
AMD Phenom II X4 965BE 3.4 GHz
AMD Phenom II X6 1055T 2.8 GHz
Intel Core i5 750 2.66 GHz
Intel Core i5 760 2.8 GHz
Intel Core i5 2500K 3.3 GHz
- High End -
AMD Phenom II X6 1090T 3.2 GHz
Intel Core i7 870 2.93 GHz
Intel Core i7 930 2.8 GHz
Intel Core i7 2600K 3.4 GHz
3. Getting the Right Motherboard
Tips on motherboard layout
View attachment 36281
1. Make sure the CPU socket type is compatible with the CPU you will be using
AM3/AM2+
- Phenom II
- Athlon II
LGA 775
- Pentium Dual Core
- Core 2 Duo
- Core 2 Quad
LGA 1156
- Core i3 500 series
- Core i5 600 series
- Core i5 700 series
- Core i7 800 series
LGA 1155
- Core i3 2000 series
- Core i5 2000 series
- Core i7 2000 series
LGA 1366
- Core i7 900 series
- Core i7 970
- Core i7 980X
2. Make sure the main 24-pin connector is located along the edge of the board. Avoid boards where the main 24-pin connector is located near the CPU socket
3. Take note of the position of the sATA ports. If you are planning on using gaming graphics cards, make sure the sATA ports are not in line with the PCI-E slots. If ever the sATA ports are in line with a PCI-E slot, make sure they are in a parallel position with respect to the board like the black sATA ports of the MSI P55-GD80 pictured above. However, there are some casings where you need the sATA ports to be perpendicular with respect to the board.
4. As much as possible, choose a board where the CMOS battery is located far from the PCI slots and PCI-E slots
5. If the budget is not restricted, select a board that uses solid capacitors. Solid capacitors are more tolerant to heat compared to electrolytic capacitors. They also have a longer life span and they don't leak.
6. For convenience, choose a board that has a CMOS reset button. Some boards even a feature a CMOS reset button located at the rear panel so you don't have to open the casing if ever you need to reset the CMOS
What Chipset Should I Choose?
The motherboard usually has 2 chipsets
1. Northbridge - for Intel LGA 775, it holds the Memory Controller and the PCI-E Controller. The Northbridge determines the type, maximum amount, and maximum speed of memory. It also determines the number of PCI-E lanes that will be available.
2. Southbridge - it handles the Input/Output devices (keyboard, mouse, gamepads), storage devices (HDD, SSD, USB) and other components of the PC
Modern AMD and Intel CPU's now have an Integrated Memory Controller. So it is now the CPU that determines the type, maximum amount, and maximum speed of memory. The Northbridge is now only left with the function of supplying the PCI-E lanes. Modern CPU's don't use the FSB anymore, they now communicate directly with the memory
For Intel LGA 1156 motherboards, there is only one main chip - the Platform Controller Hub. It functions more like a Southbridge and the 2 common chipsets are P55 and H55. The main difference between P55 and H55 is that H55 allows the use of IGP's of Intel Core i3 500 and Core i5 600. Using a Core i3 500 or Core i5 600 on a P55 board is possible but the IGP will be disabled. All LGA 1156 processors are compatible with P55 and H55.
Intel LGA 1366 boards still has two chips- the Northbridge and the Southbridge. It only has one type of Northbridge - the X58. The X58 chipset has 36 PCI-E lanes but this becomes only significant in a multi-GPU setup.
List of Recommended Motherboards
- Entry Level -
ASRock N68C-S (AM3 / AM2+)
ASRock 880GM-LE (AM3)
MSI 785G-E53 (AM3)
ASRock P55 Pro (LGA 1156)
eVGA H55-V (LGA 1156)
- Mainstream -
ASRock 890GX Extreme 3 (AM3)
MSI 890GXM-G65 (AM3)
Asus M4A89GTD PRO/USB3 (AM3)
MSI H55-GD65 (LGA 1156)
MSI P55-GD65 (LGA 1156)
MSI P55-GD80 (LGA 1156)
eVGA P55 SLI (LGA 1156)
eVGA X58 SLI Micro (LGA 1366)
- High End -
Asus Crosshair IV Formula (AM3)
MSI Big Bang Fuzion (LGA 1156)
MSI Big Bang X Power (LGA 1366)
4. Memory Speed, Type and Amount
Form Factor
These are the types of memory according to form factor. The form factor indicates the size of the module and the number of contact pins
1. SIMM - Single In-line Memory Module. It can either have 30 pins or 72 pins.
2. DIMM - Dual In-line Memory Module. This is the form factor used by modern desktop PC's. It can have a 184-pin configuration or a 240-pin configuration. Modern desktop PC's use DIMM's
3. SODIMM - Small Outline DIMM. Used by laptop PC's. It can have a 72-pin configuration or 144-pin configuration
4. MicroDIMM - smaller than SODIMM
Types of Desktop DIMM
DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate SDRAM)
1. DDR2 (1.8V) - used by Intel LGA 775 CPU's and AMD AM3/AM2+ CPU's
2. DDR3 (1.35V to 1.65) - used by Intel LGA 1156 CPU's, LGA 1366 CPU's and AMD AM3 CPU's
View attachment 36282
(DDR3 modules can only be installed in a DDR3 slot and DDR2 modules can only be installed in a DDR2 slot)
Modern PC's should have a minimum of 2GB RAM especially if you intend to use it for gaming. If there are no restrictions on the budget, go for 4GB. But I recommend you get two 2GB modules instead of one 4GB module. This would come in handy if ever one of the modules fail. If you do heavy multi-tasking, go for 6GB or 8GB.
If you are building a new PC, there si really no need to go for DDR2 because the price of the DDR2 and DDR3 are almost the same. But in terms of real world performance, DDR2 and DDR3 perform equally at the same DRAM frequency
Most manufacturers sell dual-channel kits. These are ordinary modules but they already come in pairs so you won't have compatibility issues. So, if you plan on using two memory modules, get a dual-channel kit instead of buying two separate memory modules. By the way, Intel LGA 1366 CPU's use triple-channel DDR3 modules so check before buying to avoid compatibility issues.
To check if dual channel mode is enabled, you can see it at the boot up screen or you can use CPU-Z. See image below for a sampe of CPU-Z screenshot
View attachment 36283
What Memory Speed Should I Choose ?
For the memory speed, DDR3 1333 and DDR3 1600 will do for real world applications. Only synthetic benchmarks will benefit from DDR3 1800 or higher
+ Test System +
Intel Core i7 870
Asus Maximus III Formula
Corsair 2GBx2 DDR3 1600
Zotac GeForce GTX 260
Windows Vista Enterprise Version 64-bit
WinRar 3.9 beta 64-bit - File Compression (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 117.4
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 114.9
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 110.2
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 103.8
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
WinZip 12 - File Compression (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 102.1
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 101.4
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 101.0
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 100.3
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
Adobe Acrobat 9 Professional - PDF document creation (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 101.1
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 101.1
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 101.1
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 101.1
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
Adobe Photoshop CS4 - Image Processing - Applying 6 filters to a 69MB TIF image (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 101.0
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
Lame 3.98 - Audio encoding - wav to mp3 160kbps (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
DivX 6.8.3 - Video transcoding - MPEG2 to AVI (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 103.6
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 102.4
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 102.4
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 101.2
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
3DS Max 2009 - Image rendering - 1920 x 1080 (percentage - higher is better)
DDR3 1333 7-7-7-20 ----------- 101.3
DDR3 1600 8-8-8-24 ----------- 101.3
DDR3 1066 8-8-8-24 ----------- 100.7
DDR3 1066 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
DDR3 800 6-6-6-18 ----------- 100.0
Memory Clock Speed and Data Transfer Rate
Memory - Real Clock - Effective Clock - Maximum Theoretical Data Rate - Memory Module
DDR 200 - 100 MHz - 200 MHz - 1600 MB/s - PC-1600
DDR 266 - 133 MHz - 266 MHz - 2133 MB/s - PC-2100
DDR 333 - 166 MHz - 333 MHz - 2666 MB/s - PC-2700
DDR 400 - 200 MHz = 400 MHz - 3200 MB/s - PC-3200
DDR2 400 - 200 MHz - 400 MHz - 3200 MB/s - PC2-3200
DDR2 533 - 266 MHz - 533 MHz - 4266 MB/s - PC2-4200
DDR2 667 - 333 MHz - 667 MHz - 5333 MB/s - PC2-5300
DDR2 800 - 400 MHz - 800 MHz - 6400 MB/s - PC2-6400
DDR2 1066 - 533 MHz - 1066 MHz - 8533 MB/s - PC2-8500
DDR3 800 - 400 MHz - 800 MHz - 6400 MB/s - PC3-6400
DDR3 1066 - 533 MHz - 1066 MHz - 8533 MB/s - PC3-8500
DDR3 1333 - 667 MHz - 1333 MHz - 10666 MB/s - PC3-10600
DDR3 1600 - 800 MHz - 1600 MHz - 12800 MB/s - PC3-12800
DDR3 1800 - 900 MHz - 1800 MHz - 14400 MB/s - PC3-14400
DDR3 2000 - 1000 MHz - 2000 MHz - 16000 MB/s - PC3-16000
Effective Clock = Real Clock x 2
Maximum Theoretical Data Rate = Effective Clock x 8
Memory modules manufacturers usually name their mmodules according to the Effective Clock but some use the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
How to Read Part Numbers of Memory Modules
Kingston
Part Number: KHX1600C7D3K2/4GX
--> KHX means Kingston HyperX
--> 1600 is the Effective Clock
--> C7 is the CAS Latency
--> D3 means DDR3
--> K2 means 2 modules
--> 4G is the total capacity of the modules
This is a Kingston HyperX 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL7
Kingston
Part Number: KHX1333C7D3K3/6GX
--> KHX means Kingston HyperX
--> 1333 is the Effective Clock
--> C7 is the CAS Latency
--> D3 means DDR3
--> K3 means 3 modules
--> 6G is the total capacity of the modules
This is a Kingston HyperX 2GBx3 DDR3 1333 CL7
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL9D-4GBRL
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL9 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> D means dual channel, 2 modules
--> 4GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> R stands for Ripjaws
--> L means Ripjaws rated at 1.5V
This is a G. Skill Ripjaws 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL9
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL8D-4GBRM
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL8 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> D means dual channel, 2 modules
--> 4GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> R stands for Ripjaws
This is a G. Skill Ripjaws 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL8
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL8Q-8GBRM
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL8 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> Q means dual channel, 4 modules
--> 8GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> R stands for Ripjaws
This is a G. Skill Ripjaws 2GBx4 DDR3 1600 CL8
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL7D-4GBRH
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL7 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> D means dual channel, 2 modules
--> 4GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> R stands for Ripjaws
This is a G. Skill Ripjaws 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL7
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL8D-4GBTD
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL8 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> D means dual channel, 2 modules
--> 4GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> T stands for Trident
This is a G. Skill Trident 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL8
G. Skill
Part Number: F3-12800CL7T-6GBRH
--> 12800 is the Maximum Theoretical Data Rate
--> CL7 is the CAS Latency
--> F3 means DDR3
--> T means triple channel, 3 modules
--> 6GB is the total capacity of the modules
--> R stands for Ripjaws
This is a G. Skill Ripjaws 2GBx3 DDR3 1600 CL7
Corsair
Part Number: CMG4GX3M2A1600C7
--> 1600 is the Effective Clock
--> C7 is the CAS Latency
--> 4G is the total capacity of the modules
This is a Corsair 2GBx2 DDR3 1600 CL7
Attachments
Last edited:

 Hit ko po
Hit ko po  para sau..
para sau.. 


